Neuropathy is a condition that affects millions of individuals, disrupting their daily lives with persistent pain, numbness, and weakness. At Sweeney Health Centers, we specialize in identifying and addressing neuropathy signs and symptoms, helping patients regain mobility and comfort. If you are experiencing unusual sensations in your hands, feet, or other extremities, recognizing the early indicators of neuropathy is crucial for effective intervention.

What Is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy, also known as peripheral neuropathy, occurs when nerves outside the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This condition can result from various causes, including diabetes, infections, autoimmune diseases, and traumatic injuries. Understanding neuropathy signs and symptoms can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention before the condition worsens.
Common Neuropathy Signs and Symptoms
1. Persistent Numbness and Tingling
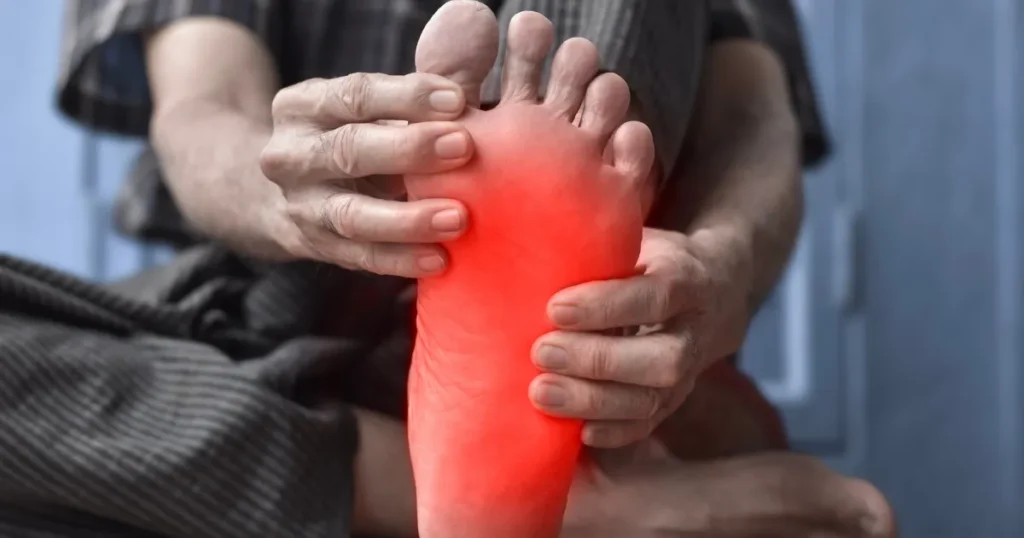
One of the earliest and most frequent neuropathy signs and symptoms is persistent numbness or tingling, typically starting in the hands or feet. This sensation often spreads upward over time, causing discomfort and reduced sensitivity in affected areas.
2. Sharp, Burning, or Stabbing Pain
Neuropathy frequently causes severe pain, which can feel like:
- Burning
- Stabbing
- Electric shock-like sensations
- Throbbing discomfort
Pain intensity varies among individuals, with some experiencing mild irritation and others struggling with chronic, debilitating agony.
3. Muscle Weakness and Loss of Coordination
As nerve damage progresses, individuals may notice a loss of strength and coordination. Simple tasks, such as gripping objects or walking, may become increasingly difficult due to muscle weakness and instability.
4. Increased Sensitivity to Touch
Many neuropathy sufferers develop hyperesthesia, an extreme sensitivity to touch. Even light contact, such as fabric brushing against the skin, can trigger intense pain or discomfort.
5. Loss of Reflexes and Balance Issues
As neuropathy affects the nerves responsible for motor function, reflexes may diminish, leading to balance problems and an increased risk of falls, particularly in elderly individuals.
6. Temperature Intolerance
Nerve damage can disrupt temperature regulation, causing individuals to experience excessive sweating or an inability to detect temperature changes, leading to potential burns or frostbite risks.
7. Digestive and Autonomic Dysfunction
In severe cases, neuropathy affects the autonomic nervous system, resulting in:
- Digestive issues (constipation, diarrhea, bloating)
- Dizziness upon standing (orthostatic hypotension)
- Bladder dysfunction
- Abnormal heart rate fluctuations
What Causes Neuropathy?
Neuropathy can develop due to various underlying conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
Diabetes
Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most prevalent forms, affecting nearly 50% of individuals with long-term diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage nerves over time, leading to neuropathy signs and symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiencies in essential vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and E, can impair nerve function, contributing to neuropathic symptoms.
Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can trigger neuropathy by attacking nerve tissues.
Infections and Viruses
Neuropathy can result from infections such as:
- Shingles (postherpetic neuralgia)
- Lyme disease
- Hepatitis C
- HIV/AIDS
Toxic Exposures and Medications
Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, as well as exposure to toxins like heavy metals and alcohol, can contribute to nerve damage.
How Is Neuropathy Diagnosed?
To diagnose neuropathy, healthcare professionals may perform:
- Physical Examinations: Assessing reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Measuring electrical signals in nerves
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluating muscle response to nerve signals
- Blood Tests: Detecting vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, or autoimmune markers
- Imaging Scans (MRI/CT): Identifying structural nerve damage
Treatment Options for Neuropathy
1. Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and avoiding alcohol and smoking can slow neuropathy progression.
2. Physical Therapy and Exercise
Regular stretching, balance training, and muscle-strengthening exercises can improve mobility and reduce neuropathic discomfort.
3. Medications and Pain Management
Common medications prescribed for neuropathy include:
- Antidepressants (amitriptyline, duloxetine)
- Anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin)
- Topical Treatments (capsaicin cream, lidocaine patches)
4. Alternative Therapies
Some patients find relief with acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) therapy.
5. Specialized Neuropathy Care at Sweeney Health Centers
At Sweeney Health Centers, we offer personalized neuropathy treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. Our team uses cutting-edge techniques to reduce pain, restore function, and improve overall quality of life.
The Long-Term Impact of Neuropathy
Ignoring neuropathy signs and symptoms can lead to severe long-term complications. Chronic pain and numbness may worsen, increasing the risk of infections, ulcers, and even amputations in severe cases. Additionally, the emotional toll of persistent pain can contribute to anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to preventing these complications and ensuring better long-term health outcomes. At Sweeney Health Centers, we emphasize proactive care to help patients manage their symptoms effectively and maintain their overall well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you are experiencing persistent neuropathy signs and symptoms, early intervention is key. Ignoring symptoms may result in irreversible nerve damage, leading to long-term complications. Seeking prompt medical attention can help slow progression and alleviate discomfort.
Contact Sweeney Health Centers Today!
If you or a loved one are struggling with neuropathy, Sweeney Health Centers is here to help. We offer specialized treatment plans to relieve nerve pain and restore function. Sign up for our new patient special and take the first step toward relief. Call us now at 615-595-9063!
Sources:
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) – https://www.ninds.nih.gov
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – https://www.niddk.nih.gov
- Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org


